Blockchain technology is the concept or protocol behind the running of the blockchain. Blockchain technology makes cryptocurrencies (digital currencies secured by cryptography) like Bitcoin work just like the internet makes email possible.
The blockchain is an immutable (unchangeable, meaning a transaction or file recorded cannot be changed) distributed digital ledger (digital record of transactions or data stored in multiple places on a computer network) with many use cases beyond cryptocurrencies.
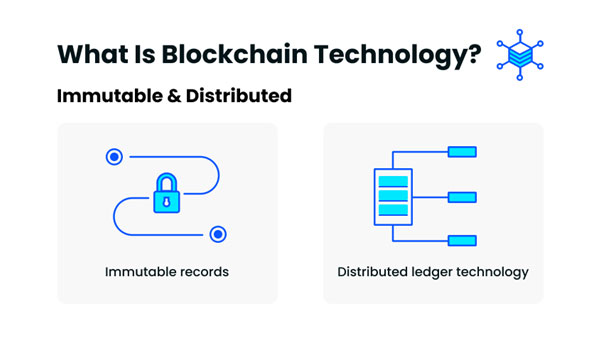
Immutable and distributed are two fundamental blockchain properties. The immutability of the ledger means you can always trust it to be accurate. Being distributed protects the blockchain from network attacks.
Each transaction or record on the ledger is stored in a “block.” For example, blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain consist of an average of more than 500 Bitcoin transactions.
The information contained in a block is dependent on and linked to the information in a previous block and, over time, forms a chain of transactions. Hence the word blockchain.
Types of Blockchains
There are four types of blockchains:
1. Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open, decentralized networks of computers accessible to anyone wanting to request or validate a transaction (check for accuracy). Those (miners) who validate transactions receive rewards.
Public blockchains use proof-of-work or proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms (discussed later). Two common examples of public blockchains include the Bitcoin and Ethereum (ETH) blockchains.
2. Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are not open, they have access restrictions. People who want to join require permission from the system administrator. They are typically governed by one entity, meaning they’re centralized. For example, Hyperledger is a private, permissioned blockchain.
3. Hybrid Blockchains or Consortiums
Consortiums are a combination of public and private blockchains and contain centralized and decentralized features. For example, Energy Web Foundation, Dragonchain, and R3.
Take note: There isn’t a 100 percent consensus on whether these are different terms. Some make a distinction between the two, while others consider them the same thing.
4. Sidechains
A sidechain is a blockchain running parallel to the main chain. It allows users to move digital assets between two different blockchains and improves scalability and efficiency. An example of a sidechain is the Liquid Network.
History of Blockchain
Blockchain isn’t just a database, it’s a new technology stack with ‘digital trust’ that is revolutionizing the way we exchange value and information across the internet, by taking out the ‘gatekeepers’ from the process. For a complete and more detailed deep dive check out our article: A Concise History of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain history goes back farther than you might imagine, but we’ve condensed it by answering four critical questions:

A blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores data in immutable “blocks” of data items that are
linked sequentially
Distributed Ledger: Generalization of (Bitcoin) Blockchain
A database that
-
- Is replicated
- Is append-only and records are immutable
- Guarantees integrity and authenticity of records
- Provides verifiability of records
Participants collectively validate and maintain a growing data set
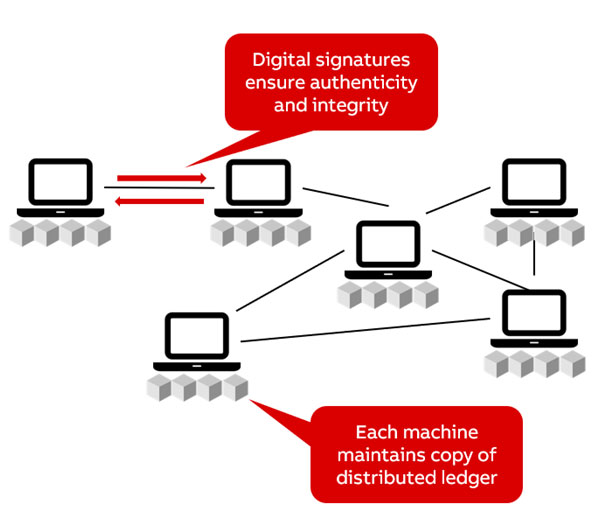
Block chain architecture
Blockchain architecture refers to the structure and design of a blockchain system, including the various components and how they interact with each other. Here are some key components of a blockchain architecture:
- Nodes: Nodes are individual computers or devices that participate in the blockchain network. Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain ledger and helps to validate and process transactions.
- Blockchain protocol: The blockchain protocol is the set of rules and procedures that govern how the blockchain operates, including how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain.
- Consensus mechanism: The consensus mechanism is the process by which nodes on the blockchain network come to a collective agreement on the state of the blockchain. Different consensus mechanisms include proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, and delegated proof-of-stake.
- Smart contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. They allow for decentralized applications to run on the blockchain and can automate complex business processes.
- Distributed ledger: The distributed ledger is a database that stores all transactions that have been processed on the blockchain. Each block on the blockchain contains a hash of the previous block, creating a chain of blocks that make up the blockchain.
- Public or private blockchain: A public blockchain is open to anyone to join and participate in the network, while a private blockchain is only accessible to a specific group of participants.
- Network topology: The network topology refers to how the nodes on the blockchain network are connected to each other. Different network topologies include peer-to-peer networks and client-server networks.
These components work together to create a secure and decentralized system that is resistant to fraud and tampering. The specific architecture of a blockchain system can vary depending on the platform and the needs of the application.
Block chain career options
Blockchain technology has become increasingly popular in recent years, and there is a growing demand for professionals with blockchain expertise. Here are some career options in the blockchain industry:
- Blockchain Developer: Blockchain developers are responsible for creating, designing, and implementing blockchain solutions. They need to have knowledge of programming languages such as Solidity, Java, C++, and JavaScript. They also need to be familiar with blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Corda.
- Blockchain Architect: Blockchain architects design and oversee the development of blockchain systems. They need to have a deep understanding of blockchain technology and its use cases. They also need to be familiar with programming languages and blockchain platforms.
- Blockchain Consultant: Blockchain consultants provide guidance and advice to organizations that want to implement blockchain solutions. They need to have a good understanding of blockchain technology, its use cases, and its potential benefits and limitations.
- Blockchain Project Manager: Blockchain project managers are responsible for overseeing the development and implementation of blockchain projects. They need to have project management skills, as well as knowledge of blockchain technology and its use cases.
- Blockchain Analyst: Blockchain analysts analyze data and information related to blockchain projects. They need to have knowledge of blockchain technology, as well as data analysis and visualization tools.
- Blockchain Security Specialist: Blockchain security specialists are responsible for ensuring the security of blockchain systems. They need to have knowledge of blockchain technology and its potential security risks, as well as security protocols and tools.
- Blockchain Marketing Manager: Blockchain marketing managers are responsible for promoting and marketing blockchain solutions. They need to have knowledge of blockchain technology and its potential use cases, as well as marketing and communication skills.
These are just some of the many career options available in the blockchain industry. The demand for blockchain professionals is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, making it an exciting field to pursue.
Block chain Programming languages
Blockchain technology is built upon a set of programming languages that enable developers to create decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and other blockchain-based solutions. Here are some of the most popular programming languages used in blockchain development:
- Solidity: Solidity is a high-level programming language specifically designed for smart contracts on the Ethereum platform. It is similar to JavaScript and uses syntax similar to C++, making it relatively easy to learn for experienced developers.
- Java: Java is a popular programming language used for developing enterprise-grade blockchain applications. It is a versatile language that is easy to learn and has a large community of developers and libraries.
- C++: C++ is a powerful programming language that is widely used in blockchain development due to its speed and efficiency. It is often used in developing blockchain nodes and other infrastructure components.
- Python: Python is a popular programming language used for developing blockchain applications due to its simplicity and ease of use. It is often used in developing dApps and smart contracts on platforms such as Ethereum.
- JavaScript: JavaScript is a popular programming language that is often used in developing blockchain-based web applications. It is used for creating front-end interfaces and is also used in building dApps on platforms such as Ethereum.
- Go: Go is a relatively new programming language that is gaining popularity in blockchain development due to its simplicity, speed, and concurrency features. It is often used in developing blockchain nodes and other infrastructure components.
These programming languages provide a variety of features and tools that can help streamline the blockchain development process and make it more efficient. Ultimately, the choice of programming language will depend on personal preference, the specific needs of the project, and the blockchain platform being used.
Courses, Training or Learning options for Block chain
There are many online courses and resources available for learning blockchain technology. Here are some popular options:
- Blockchain Basics: This free course from edX provides an introduction to blockchain technology, including how it works, its applications, and potential impact.
- Blockchain Fundamentals: Offered by IBM, this course provides an in-depth introduction to blockchain technology and its applications, as well as hands-on experience with Hyperledger Fabric.
- Blockchain Essentials: This course from LinkedIn Learning provides an overview of blockchain technology and its applications, including cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and dApps.
- Ethereum and Solidity: The Complete Developer’s Guide: This Udemy course is a comprehensive guide to developing decentralized applications on the Ethereum blockchain using Solidity.
- ConsenSys Academy: ConsenSys Academy offers a range of blockchain courses, including Ethereum development, blockchain for business, and blockchain for social impact.
- B9lab Academy: B9lab Academy offers a range of blockchain courses, including Ethereum development, Hyperledger Fabric, and blockchain for executives.
- Blockgeeks: Blockgeeks provides a variety of courses and resources for learning blockchain technology, including a blockchain 101 course, blockchain developer bootcamp, and courses on specific blockchain platforms.
These are just a few examples of the many online courses and resources available for learning blockchain technology. Additionally, there are many blockchain conferences, workshops, and meetups that provide opportunities to learn and network with other blockchain professionals.
Block chain IDE
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a software application that provides a comprehensive development environment for programming. Here are some popular IDEs that can be used for blockchain development:
- Remix IDE: Remix IDE is a popular open-source IDE that is widely used for blockchain development. It is specifically designed for Solidity programming and supports smart contract development on the Ethereum platform.
- Visual Studio Code: Visual Studio Code is a lightweight, cross-platform IDE that supports multiple programming languages, including Solidity. It has a variety of features useful for blockchain development, such as syntax highlighting, code snippets, and debugging support.
- Truffle Suite: Truffle Suite is a suite of tools and IDEs specifically designed for blockchain development. It includes Truffle Framework, which provides a development environment for smart contracts, and Ganache, which provides a local blockchain environment for testing.
- Embark: Embark is a blockchain development framework that provides an IDE for building decentralized applications (dApps). It supports multiple blockchain platforms, including Ethereum and IPFS, and provides a variety of tools and features for blockchain development.
- Ethereum Studio: Ethereum Studio is a web-based IDE specifically designed for developing Ethereum smart contracts. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and testing smart contracts and includes a variety of tools and features for blockchain development.
These IDEs provide a variety of features and tools that can help streamline the blockchain development process and make it more efficient. Ultimately, the choice of IDE will depend on personal preference, the specific needs of the project, and the programming languages and platforms being used.


