SAP Production Planning is a module that handles all business processes related to production processes of a company involved in manufacturing or assembly. SAP PP Module originates from Sales and Operations planning of a company and helps to plan the resources relevant for manufacturing in an organized fashion.
SAP PP includes all activities like Material Requirement Planning(MRP), Bill of Materials(BOM), Capacity Planning(CP) and Supply Chain Planning(SCP).
All these processes need master data to be maintained and the training helps to apply and communicate this master data in the area of planning and manufacturing.
Production planning is the process of deciding how a product or service will be manufactured before the manufacturing process begins. In other words, it is how you plan to manage your supply chain, raw materials, employees and the physical space where the manufacturing process takes place
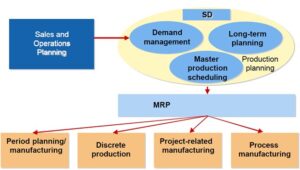
The SAP PP (Production Planning) module consists of several sub-modules that provide specialized functionalities for different aspects of production planning and control. The main sub-modules of SAP PP include:
- Master Data:
- Material Master: Manages information about materials used in production, including material type, BOMs, work centers, and planning data.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): Defines the structure and components required to produce a finished product.
- Work Centers: Stores information about production resources such as machines, labor, and tools.
- Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP):
- Demand Management: Forecasts and manages demand for products to support production planning.
- Sales Planning: Helps plan and align production with sales forecasts and customer demands.
- Production Planning: Creates a production plan based on the demand forecast and available resources.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP):
- Material Requirements Planning: Calculates and generates procurement proposals or planned orders based on demand, lead times, and available inventory.
- Consumption-Based Planning: Triggers material replenishment based on consumption rates and predefined triggers.
- Capacity Planning:
- Capacity Planning: Determines the capacity requirements for work centers and resources to meet production demand.
- Capacity Leveling: Balances workloads and optimizes resource utilization across work centers.
- Finite Capacity Scheduling: Optimizes the production schedule by considering work center capacities and constraints.
- Production Orders:
- Production Order Creation: Creates production orders for the execution of specific production processes.
- Order Release: Releases production orders for execution on the shop floor.
- Order Confirmation: Records actual production activities, including consumption of materials, labor, and machine hours.
- Order Settlement: Settles costs and updates the financial records associated with production orders.
- Repetitive Manufacturing:
- Production Versions: Manages different versions of production processes and routings for a product.
- Line Design: Defines the layout and sequencing of production lines for repetitive manufacturing.
- Kanban: Controls material flow in a pull-based production system using Kanban cards.
- Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP):
- Capacity Evaluation: Determines the capacity requirements for production based on planned orders and production orders.
- Capacity Leveling: Optimizes the utilization of resources to match production demand.
- Shop Floor Control:
- Shop Floor Information System: Provides real-time visibility into production activities and performance metrics.
- Shop Floor Execution: Supports the execution and tracking of production operations on the shop floor.
- Quality Management Integration: Integrates with the SAP QM module to manage quality inspections and control points during production.
These sub-modules work together to support various stages of production planning, execution, and control, enabling organizations to optimize their production processes, improve efficiency, and meet customer demands effectively.
Implementing the SAP PP (Production Planning) module requires certain pre-requisites to ensure a smooth and successful implementation. Here are the key pre-requisites for implementing the SAP PP module:
- SAP System Landscape: Ensure that you have a suitable SAP system landscape in place. This includes the availability of the necessary SAP components, such as SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) or the latest S/4HANA version, as well as the required underlying technology infrastructure (hardware, operating systems, databases).
- Business Blueprint: Develop a comprehensive business blueprint that outlines the scope and objectives of the SAP PP implementation. Define the key business processes, organizational structure, master data requirements, and integration points with other SAP modules or external systems.
- Project Team: Assemble a project team with the necessary skills and expertise to implement the SAP PP module. This typically includes business process experts, IT professionals, functional consultants, and key business users from production planning, logistics, and other relevant departments.
- Process Analysis and Design: Conduct a thorough analysis of your existing production planning processes. Identify areas for improvement, bottlenecks, and pain points. Design optimized and standardized processes that align with industry best practices and can be implemented using the SAP PP module.
- Master Data Readiness: Ensure that the required master data is complete, accurate, and consistent. This includes material master records, bills of materials (BOMs), work centers, routing data, production versions, and other relevant data. Cleanse and enhance the master data as necessary to ensure a smooth migration to the SAP PP module.
- Infrastructure Readiness: Assess your IT infrastructure and ensure that it meets the technical requirements for implementing the SAP PP module. This includes server capacity, network connectivity, database management, and hardware/software compatibility. Plan for any necessary upgrades or enhancements.
- Integration Requirements: Identify the integration points between the SAP PP module and other SAP modules or external systems within your organization. Define the data flow, interfaces, and integration scenarios required for seamless information exchange. This may include integration with modules like Materials Management (MM), Sales & Distribution (SD), Finance and Controlling (FI/CO), Quality Management (QM), and Plant Maintenance (PM).
- Training and Change Management: Develop a comprehensive training plan to ensure that key users and stakeholders are trained on the SAP PP module. This includes providing training on the functionality, processes, and usage of the module. Also, plan for change management activities to address any resistance to change, communicate the benefits, and facilitate a smooth transition to the new system.
- Documentation and Knowledge Transfer: Establish documentation standards and ensure that all relevant processes, configurations, and user manuals are properly documented. This will help in knowledge transfer and support ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Test and Validation Plan: Develop a detailed test and validation plan to ensure the correctness and reliability of the implemented SAP PP module. This includes designing and executing various test scenarios, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing. Validate the results against defined business requirements.
- Data Migration Strategy: Define a data migration strategy to transfer relevant data from the existing systems to the SAP PP module. This includes mapping data fields, extracting data from legacy systems, cleansing and transforming data, and loading it into the SAP system. Ensure data integrity and consistency during the migration process.
- Project Governance and Management: Establish a project governance framework and project management methodology to ensure effective planning, monitoring, and control of the SAP PP implementation. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting up project milestones and deliverables, and tracking progress against defined timelines and budgets.
By addressing these pre-requisites, you can lay a solid foundation for a successful SAP PP implementation, enabling optimized production planning processes and improved operational efficiency


[…] Production Planning Module […]